Context
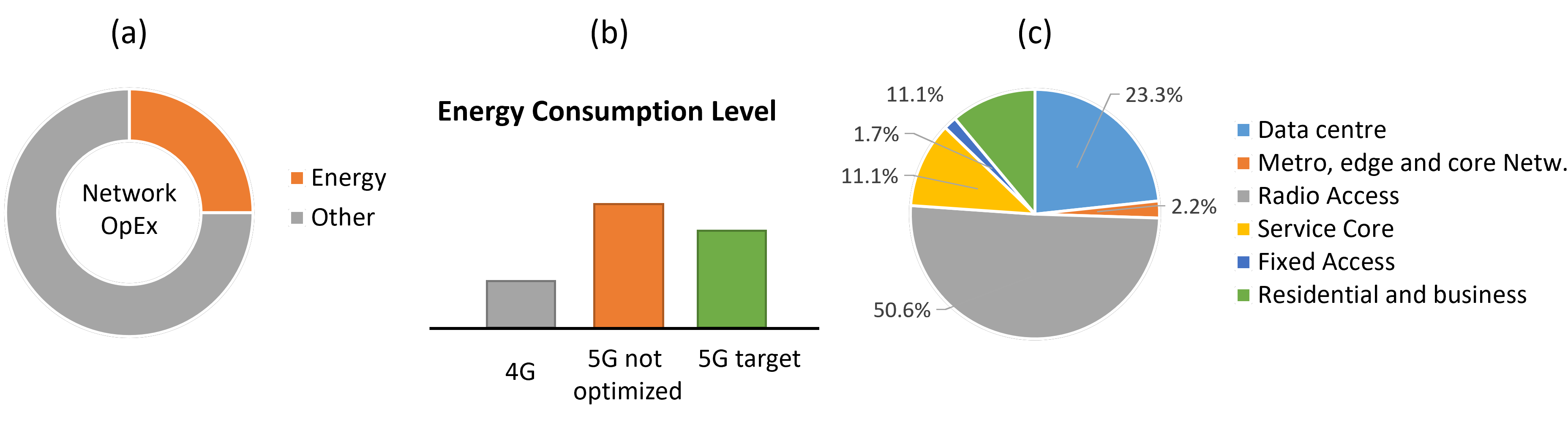
The Fifth-Generation (5G) of radio mobile networks and edge computing technologies are the two key enablers transforming the cloud into a flexible communication and inter-compute continuum, offering the possibility to introduce radically new applications in any vertical industrial domain. Recent studies indicate that the intrinsic distributed and pervasive nature of 5/6G and edge computing are going to cause a noticeable usage and deployment increase of computing resources, increasing the associated infrastructure OpEx and CapEx, and, consequently, their carbon footprint and energy requirements.
The rise of edge computing is further affecting the infrastructure and its impact on energy consumption and GreenHouse Gas (GHG) emissions, leading to an edge-cloud continuum composed of a large number of public/private micro/small/medium datacenters. Since, in 5G, edge facilities should be dimensioned against the workload produced by locally connected mobile users and their (edge) applications, The edge part of the 5/6G continuum cannot benefit from workload aggregation, and it will sensibly affect the sustainability of the ecosystem.
To cope with this problem and to meet sustainable growth targets of both the ONU 2030 Agenda and the European Green Deal, the 5/6G continuum needs to rapidly evolve new foundation paradigms specifically addressing energy and carbon footprints of the overall ecosystem.
6Green Objectives
The 6Green project aims to conceive, design, and realize an innovative service-based and holistic ecosystem, able to extend the communication infrastructure into a sustainable, interconnected, greener end-to-end inter-compute system, supporting all types of services and interconnected networks and promote energy efficiency across the whole 5/6G value-chain. The ultimate objective of the project is to enable and to foster 5/6G networks and vertical applications, reducing their carbon footprint by a factor of 10 or more with respect to business-as-usual scenarios.
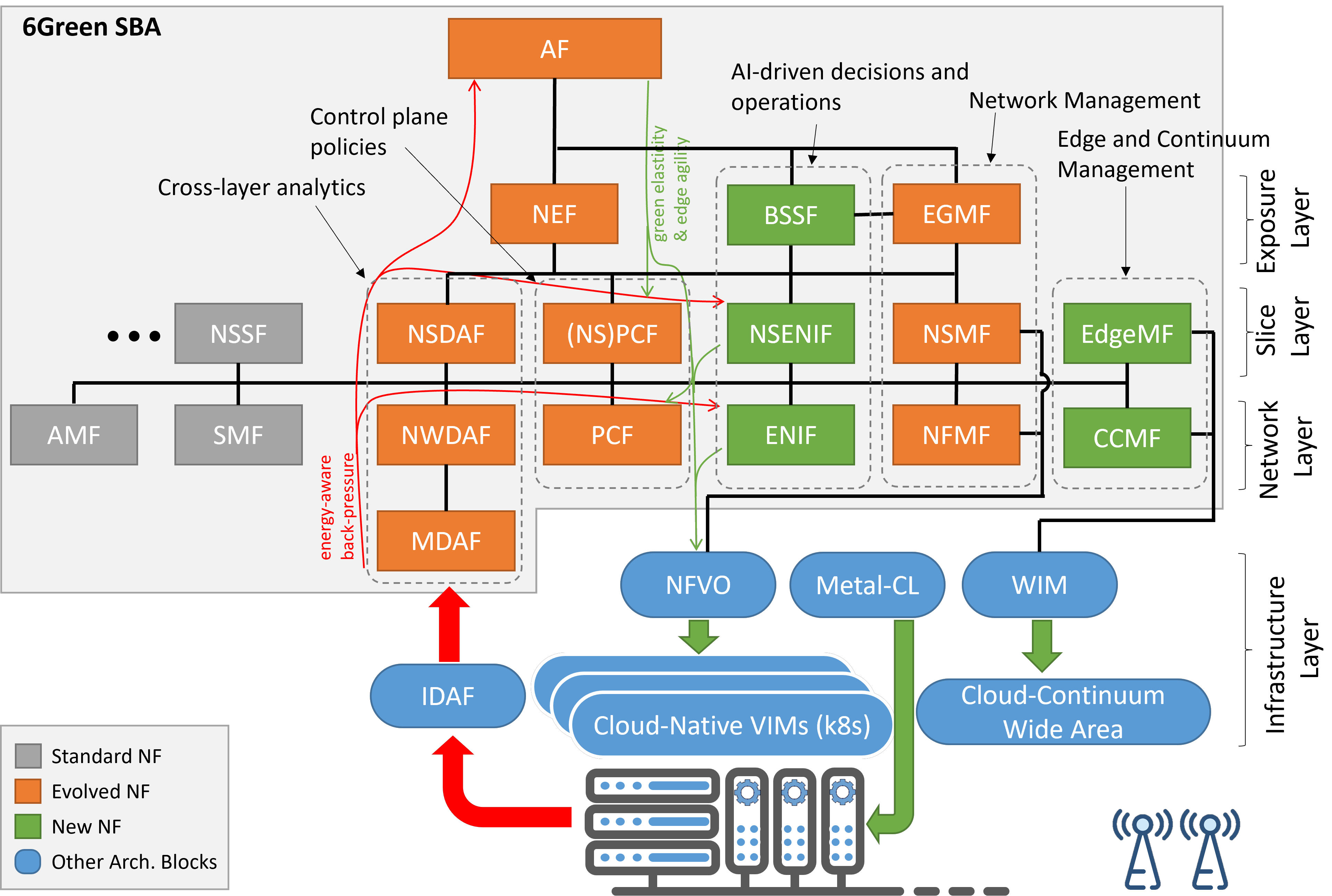
To achieve this ultimate goal, the project will exploit and extend state-of-the-art cloud-native technologies and the B5G Service-Based Architecture (SBA) with new cross-domain enablers to boost the global ecosystem flexibility, scalability and sustainability, and to make all the 5/6G stakeholders (from the ones acting at the infrastructure and network platform to vertical industries) into reducing their carbon footprint by becoming integral parts of a win-win green-economy business, and meeting a Decarbonization Service Agreement (DSA). The interactions among stakeholders will allow to achieve a tight proportionality between the dynamic and geographically distributed (mobile) workload produced by vertical applications and network slices, and the energy consumption/carbon footprint induced to the evolved SNS network and computing infrastructure.
6Green Description and Methodologies
The 6Green project envisions the 5/6G ecosystem as a sustainable, interconnected, greener, flexible end-to-end intercompute system, able to properly interface stakeholders by means of latest generation intent-based and cloud-native paradigms, and facilitating their interactions according to the aforementioned green economy business models and agreements. This will enable 5/6G vertical applications and network slices to be dynamically, scalably, and autonomically placed in the edge-cloud continuum, instantiated, modified, dimensioned, mi-grated, and released in a coordinated fashion, when and where really needed by end-users to minimize the induced impact at the infrastructure layer.
In order to shift from the current, flat/semi-static lifecycle management of network slices and applications to novel and real-time adaptive operations, three ground-breaking technological innovations have been identified that reflect the structure of the Project activities:
1. Edge Agility:
a sort of handover procedure providing smart, fast, and automated horizontal scalability to vertical application and related slices across the 5/6G edge-cloud continuum. The workload, as well as the latency budget, are redistributed according to user or infrastructure-driven events, (e.g., user mobility, seamless workload replacement/migrations, etc.). The slice/vertical application footprint is rapidly scaled to zero in all not used continuum areas and quickly resumed the operating capacity when needed.
2. Green Elasticity:
the provision of energy-aware, hardware-assisted acceleration to network functions and vertical applications to enable smart vertical scalability across the whole 5/6G ecosystem. Relying on hardware acceleration engines, which exhibit low power-consumption dependency against their usage, allows to lower processing latency with respect to pure software artefacts and to reduce consumption by exploiting standby/low power modes joint with optimal configurations/deployments.
3. Energy-Aware Backpressure:
the design of a set of cross-domain observability mechanisms and analytics, fed by hardware-level energy consumption metrics, to evaluate the energy and the carbon footprint ascribable to a vertical application or a slice. The introduction of green business models is seen as a catalyst to motivate all the stakeholders to adopt environmentally conscious behaviors through economic incentives.
Three future-proof vertical applications have been identified as project use-cases, not only because they represent future-proof 5/6G applications extremely relevant to energy- and carbon-awareness, but also because they provide challenging requirements on network slices and (edge) computing and storage facilities, which can vary according to the Energy-Aware Backpressure information flows and activated application functionalities, and that can differently trigger Edge Agility and Green Elasticity zero-touch operations.




![EN_FundedbytheEU_RGB_WHITE_Outline[1]](https://www.6green.eu/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/EN_FundedbytheEU_RGB_WHITE_Outline1.png)